Understanding Drug Testing Specimens: A Comprehensive Guide
AD
Introduction to Drug Testing Specimens
Drug testing is a crucial process used across various industries to ensure safety, compliance, and productivity. Understanding the different types of specimens used in drug testing can help individuals and organizations make informed decisions about which method best suits their needs.
Each specimen type offers unique advantages and challenges, making it essential to understand their specific applications and limitations. This guide will explore the most common drug testing specimens, providing a comprehensive overview of each.

Urine Testing
Urine testing is the most widely used method for drug testing due to its ease of collection and relatively low cost. It is effective for detecting recent drug use, typically within the past few days. The process involves collecting a urine sample, which is then analyzed for the presence of drug metabolites.
While urine tests are popular, they are not without limitations. They can be affected by factors such as hydration levels and potential sample tampering. Despite these challenges, urine drug testing remains a reliable option for many organizations.
Advantages and Limitations
Advantages:
- Non-invasive and easy to administer
- Cost-effective
- Widely accepted and understood
Limitations:
- Potential for sample adulteration or substitution
- Limited detection window

Hair Testing
Hair testing offers a longer detection window compared to other methods, capable of identifying drug use over the past 90 days. The process involves collecting a small hair sample, typically from the scalp, which is then tested for drug metabolites.
This method is less susceptible to tampering, making it a preferred option for long-term drug use detection. However, it is generally more expensive and requires specialized equipment for analysis.
Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Long detection window
- Difficult to adulterate or mask results
Cons:
- Higher cost compared to other methods
- Not effective for detecting recent drug use

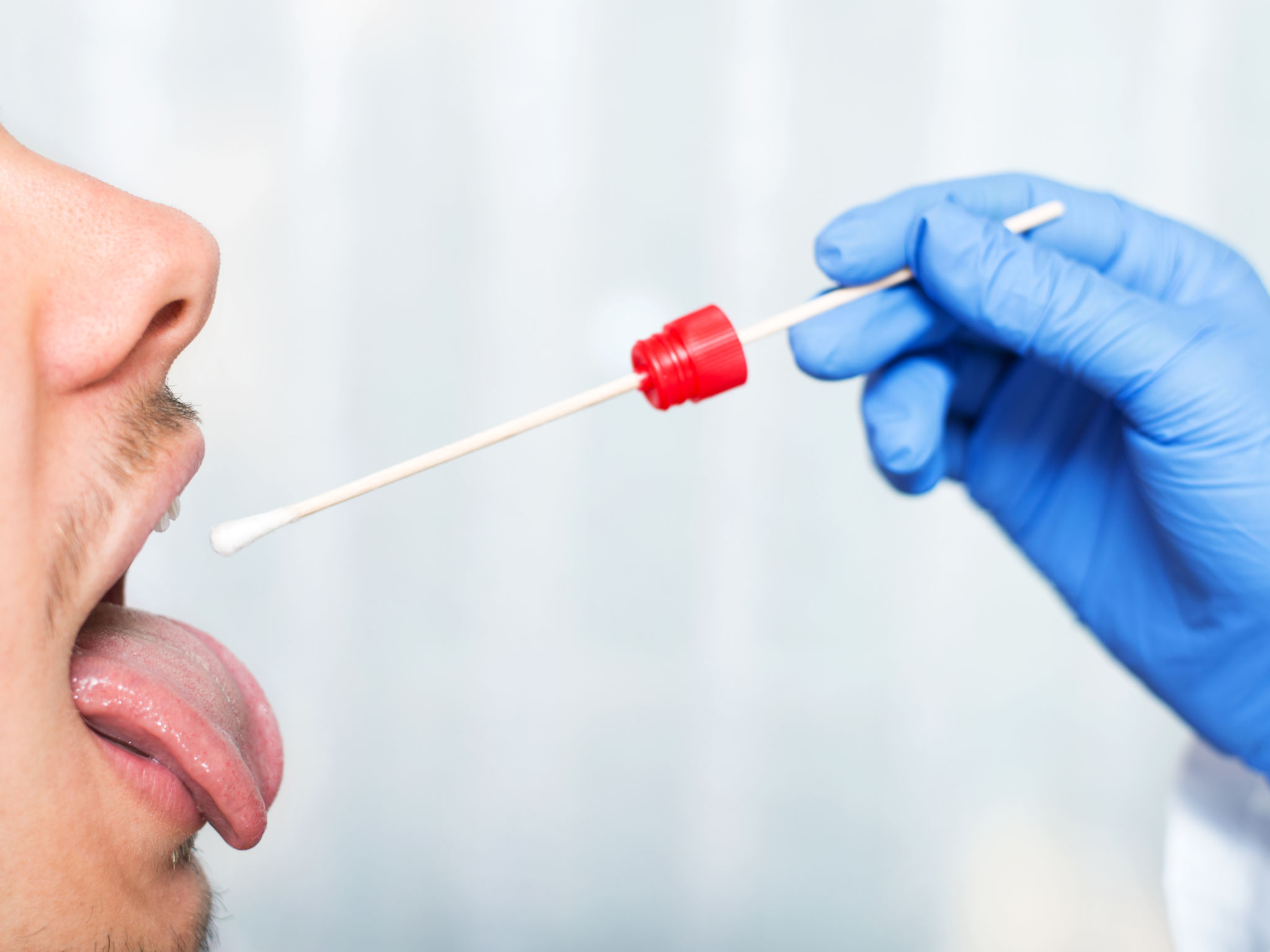
Saliva Testing
Saliva testing is gaining popularity due to its non-invasive nature and ease of administration. This method involves collecting a saliva sample from the individual, typically with a swab. Saliva testing is effective for detecting recent drug use, usually within the past 24 to 48 hours.
The convenience of saliva testing makes it an attractive option for on-site testing. However, its shorter detection window may not be suitable for all testing needs.
Benefits and Drawbacks
Benefits:
- Non-invasive and easy to collect
- Suitable for on-site testing
Drawbacks:
- Shorter detection window
- Potential variability in results based on collection technique
Blood Testing
Blood testing is one of the most accurate methods for detecting the presence of drugs in the system. It provides a precise measurement of the substance present at the time of testing. However, due to its invasive nature and higher costs, blood testing is typically reserved for specific situations such as legal or medical cases.
This method requires trained personnel to collect the sample and specialized equipment for analysis, making it less practical for routine workplace drug testing.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages:
- High accuracy and reliability
- Measures actual drug concentration in the bloodstream
Disadvantages:
- Invasive and requires trained personnel
- Higher cost and logistical complexity
Choosing the Right Specimen Type
Selecting the appropriate specimen type for drug testing depends on various factors including the detection window needed, budget constraints, and the purpose of the test. Each method offers unique benefits that can cater to different requirements.
Understanding these options can help organizations implement an effective drug testing program that aligns with their specific goals and ensures safety and compliance.
